Read History with Jack 6 - Ancient Egypt Religion
古埃及宗教
古埃及是一个信奉多神的国家,不同的城市敬拜不同的神灵。古埃及人还相信神是万能的,并且护佑着他们。因此,为了显示出他们对神的虔诚,他们做了许多事情,比如盖恢弘的神庙,建巨大的神雕像。


不同阶级的人用不同的方式来祭拜他们的神灵。法老、大祭司、还有贵族阶层在神庙中举行宗教仪式和祭祀,这就意味着他们可以与神直接沟通和碰面。法老们不能每天都去神庙祭拜,所以有时大祭司会代替法老给神供奉祭品进行祭祀。底层的老百姓则用一种完全不同的方式来祭拜神灵。他们无法进入神庙去祭祀,因为他们阶层不够。因此,他们只能在特殊节日上看到神的雕像并做祭拜。在其他日子里他们可以做一些神的小雕塑并且把他们放在神庙的前庭院里。

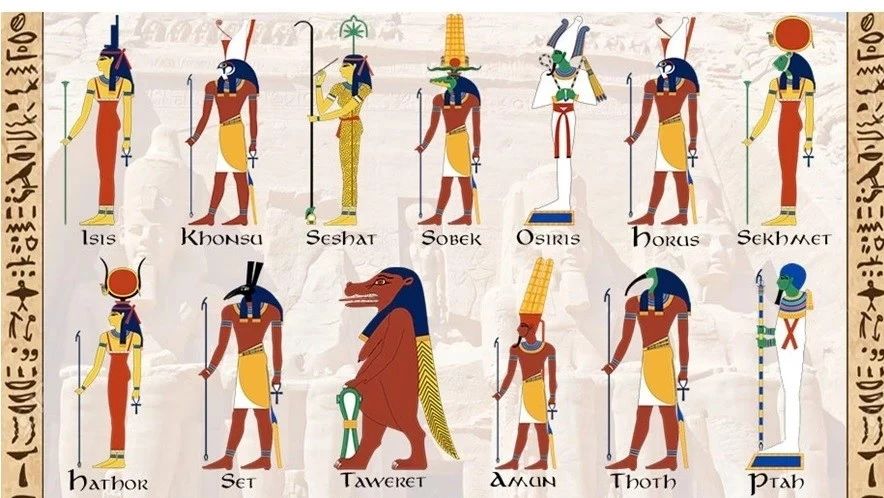
古埃及有许多神灵。拉是太阳神并且是古埃及最重要的神灵之一。奥西里斯是死亡与复活之神,他还是阴间之王。伊西斯是奥西里斯的妻子,是荷鲁斯的母亲,她是爱、保护、与魔法之神。荷鲁斯是奥西里斯和伊西斯之子,他是天空、太阳、王权、保护、和恢复之神。赛特是奥西里斯的兄弟,他是力量与战争之神。奈芙提斯是赛特的妻子,她是灵魂保护、家庭平安之神。阿努比斯是赛特和奈芙提斯的儿子,他是灵魂的守卫者与木乃伊之神。狮头人身的塞荷玛内特女神是战争,毁灭,与恢复之神……。每一位神灵各司其职,护佑着古埃及的人们。
古埃及人的生和死都与神灵们息息相关,尤其是死后。在他们的灵魂进入来世之前,必须通过一个审判。这个审判最重要的一个部分就是称心仪式。死者的心会在一个巨大天平上被称重,天平的另一边则放置一根代表正义的羽毛。古埃及信奉“轻盈的灵魂”,如果死者的心重于羽毛,就代表前世充满罪恶,心会被一头怪兽吃掉。然而如果死者的心轻于羽毛,就代表他或她通过了审判,可以去来世了。
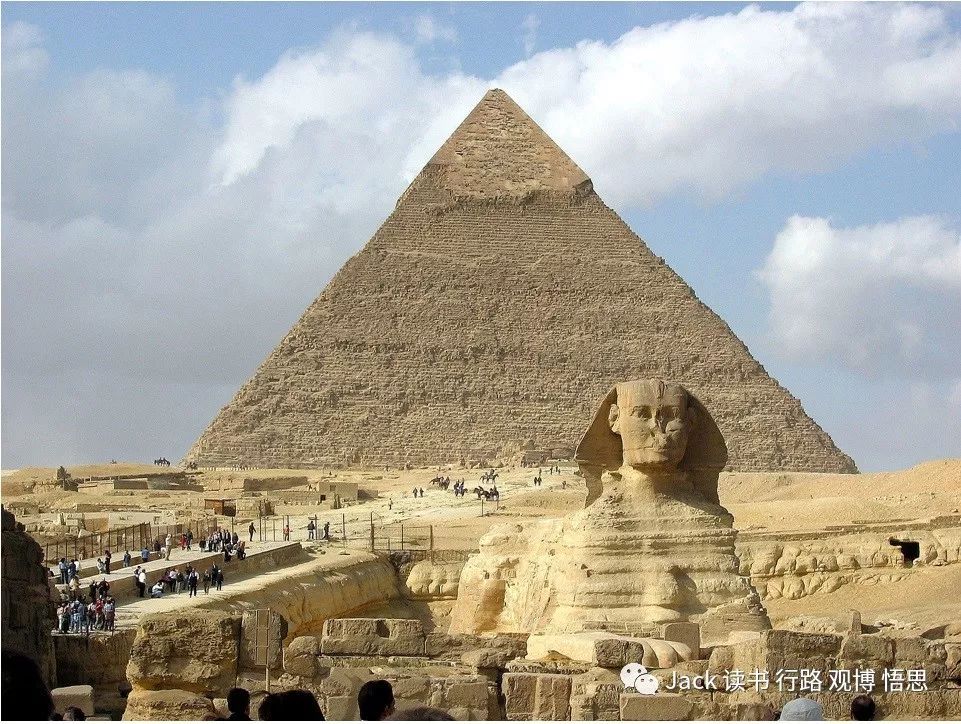
古埃及人崇拜他们的神灵,并且相信来世的存在。他们建了非常多的金字塔,神庙,方尖碑等等。这的确形成了他们的一个文化亮点,没有这些东西,我们可能也不会发现并惊叹于这么伟大灿烂的文明。但是,金字塔、神庙等消耗了大量的人力、物力、和财力,这也是导致埃及最终走向灭亡的重要原因之一。
Ancient Egypt Religion
Ancient Egypt was a polytheistic country. There were different cities with different deities that people look up to. The Ancient Egyptians believed that the gods had power over everything and protected them. Therefore, in order to show their reverence to their gods, they did many things such as building temples.



The temples were used for sacrificial ceremonies and religious rituals. However, people in different hierarchies had different ways of worshipping their deities. For instance, the Pharaohs, the High Priests, and others who were powerful performed their rituals inside the temple, which meant that they could get a direct connection to the gods. But the Pharaoh couldn’t go to the temple every day, so the High Priest represented the Pharaoh to make offerings and pray to the gods on his behalf. The citizens or farmers had a completely different way of performing the rituals. They couldn’t go inside the temple to worship because they had not reached a high rank in society. Therefore, they could only get a chance to worship during important festivals. And during common days they could carve out little sculptures of the deity and put them in the temple’s courtyard.

Ancient Egypt had many gods. For example, Ra, who was the Sun God and one of the most important deities in Ancient Egypt. Then there was Osiris, who was the god of death, resurrection, and the Nile. He ruled the underworld, and enlivened vegetation. Isis was the wife of Osiris and the mother of Horus. She was linked with motherhood, protection, and magic. Horus was the son of Osiris and Isis, and he was linked with the sky, sun, kingship, protection, and healing. Set was the brother of Osiris and he was the god of war, strength, and ambivalence. Nephthys was Set’s wife and she was the god of soul protection, lamentation, nighttime, and rivers. Anubis was Set and Nephthy’s son. He was the god of embalming and he was also the protector of the dead. The lioness goddess Sekhmet was a warrior goddess and the goddess of healing.
The Ancient Egyptians’ lives and deaths were closely connected to the deities, especially were their deaths were concerned. Before their souls went into afterlife, there was a trial that they needed to pass first. This trial would weigh the dead person’s heart to see if the person did anything bad during their lives. The person’s heart was weighed against a feather symbolizing justice. If the heart was heavier than the feather, it would be eaten by a monster. If the heart was lighter than the feather, he or she passed and enjoyed their afterlife.
Ancient Egyptians worshipped their deities, and believed in an afterlife. They built the pyramids, the temples, the obelisks, and so on. It formed one of their cultural highlights. Without these things, we might not remember this very great civilization. However, building and creating all these long-lasting things consumed lots of the country’s manpower and material resources, and in the end caused helped to cause Ancient Egypt decline.

- 本文标签: 原创
- 本文链接: http://www.jack-utopia.cn//article/542
- 版权声明: 本文由Jack原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权